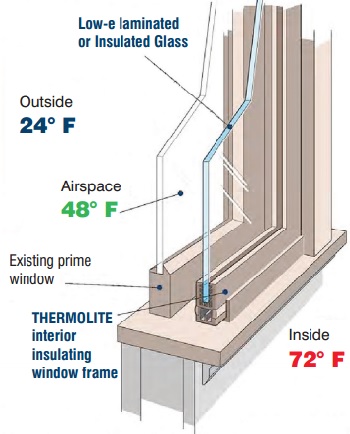
Thermolite’s patented window systems install on the interior of existing windows to deliver superior performance and appearance at a fraction of the cost of replacement windows. Secondary window systems address building envelope issues, including energy conservation and comfort, by increasing insulation value.
Our interior window systems are able to multiply the performance of existing windows by reducing heating and cooling use as well as demand. In general, total building energy performance can improve by up to 25% in cold weather climates when our secondary windows are utilized.
- Full range of laminated, suspended film, insulated and low-emissivity coatings
- Between-glass blinds lower solar heat gain in the summer and raise it in the winter
- Easily attaches to fixed, storefront and curtain wall framework
- All aluminum construction- custom colors and contours
- Sound control window systems available at STC 49
- Hurricane commercial storm windows and blast mitigation security window options without affecting sight lines
- Made in the USA – Veteran Owned
- GSA Federal Supplier Schedule Contract # GS-07F-0116H
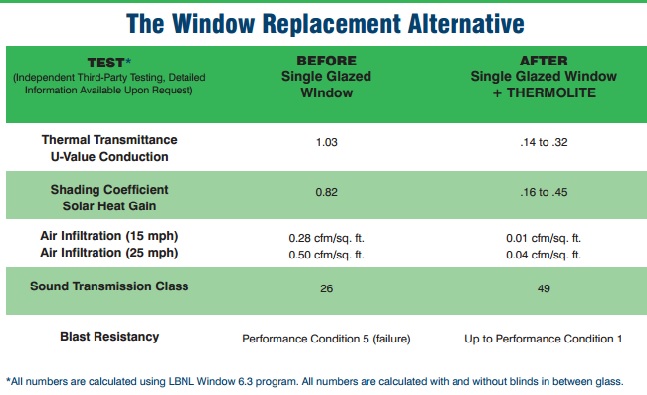
U Value: the standard method used to quantify insulating values, and measures the rate of heat flow through the window. It includes conductive, convective, and radiation heat transfer. It represents the heat flow per hour (in Btus/hr) through each square foot of window for a 1°F temperature difference between the indoor and outdoor air temperature.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient: the fraction (expressed as a number between 0 and 1) of solar radiation transmitted directly and/or absorbed through a window. The lower the SHGC, the less solar heat it transmits and the greater its shading ability. The building’s climate, orientation, and external shading will determine the optimal SHGC for a particular window, door, or skylight.
Air Infiltration: the rate of air movement around a window in the presence of a specific pressure difference across it expressed in units of cubic feet per minute per square foot of frame area (cfm/ft2). A product with a low air leakage rating is tighter than one with a high air leakage rating.
Sound Transmission Class: used to measure sound transmission loss over a frequency range from 125 to 4000 hertz, such as interior noise. The higher the rating, the less noise is perceptible.
Blast Resistancy: performance criteria rating set by the General Services Administration (GSA) to measure how window systems are able to withstand to airblast loads. It is determined by the distance debris and building fragments travels through the window after a blast and expressed as a rating from 1 to 5, with higher numbers indicating increased hazard levels.